从第三极到北极: 热喀斯特及其对碳循环影响研究进展
Studies of thermokarst and its effects on ecosystem carbon cycle in the Third Polar regions and the Arctic
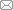
图3. 1997—2015年青藏高原祁连山区俄博岭地区热融滑塌发育过程(以2009年卫星影像作为基准影像)。1997—2009年和2009—2015年滑塌最宽处分别增加了24 m和30 m, 源头分别后退了23 m和29 m
Fig.3. The development of thaw slump on the Eboling mountains of the Qilian Mountains on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1997 to 2015 (based on 2009 satellite imagery). The widest part of the slump widened by 24 m from 1997 to 2009, and widened by 30 m from 2009 to 2015; the source of the slump retreated 23 m from 1997 to 2009, and from 2009 to 2015 going back 29 m