巴伦支-喀拉海海温和青藏高原冬季地表气温的年代际联系
Interdecadal relationship between sea surface temperature (SST) of Barents-Kara Sea and wintertime air surface temperature of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
巴伦支-喀拉海海温和青藏高原冬季地表气温的年代际联系 |
| 郑锦文, 左志燕, 蔺邹兴, 肖栋 |
|
Interdecadal relationship between sea surface temperature (SST) of Barents-Kara Sea and wintertime air surface temperature of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau |
| Jinwen ZHENG, Zhiyan ZUO, Zouxing LIN, Dong XIAO |
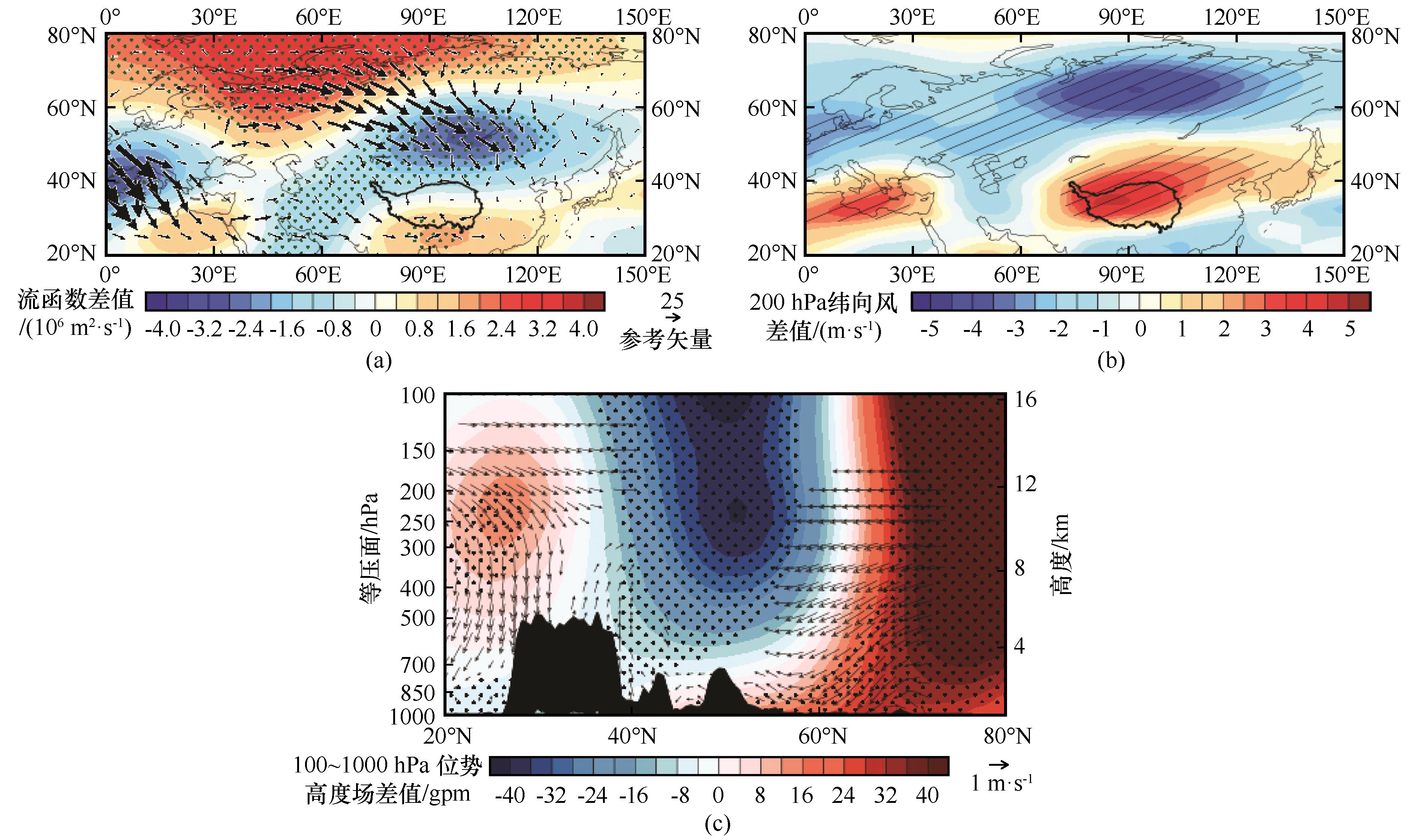
| 图8 巴伦支-喀拉海海温正位相与负位相在青藏高原范围内纬向平均(72.5°~105° E)的合成差值(1968—1977年以及2002—2010年减1978—2001年):流函数(单位:106 m2·s-1,填色)以及波活动通量(单位:m2·s-2,矢量)(a)、200 hPa纬向风(单位:m·s-1)(b)及100~1 000 hPa位势高度场(单位:gpm,填色)和风场(单位:m·s-1,矢量)(c)[打点和阴影区域以及矢量表示通过了订正自由度后的95%的Student’s t检验;(c)下部的黑色实线代表87.5° E处的地形] |
| Fig. 8 The composite differences of zonal mean over Tibetan Plateau (72.5°~105° E) between positive and negative phases of SST of Barents-Kara Sea (1968—1977 and 2002—2010 minus 1978—2001): stream function (unit: 106 m2·s-1, shading) and wave activity flux (unit: m2·s-2, vector) (a), 200 hPa zonal wind (unit: m·s-1) (b) and 100~1 000 hPa potential height field (unit: gpm, shading) and wind filed (unit: m·s-1, vector) (c) [The dotted and shaded areas and vectors indicate passing 95% Student’s t-test after the revised degrees of freedom; The black solid lines in (c) lower part represent the terrain at 87.5° E] |

|