AMAP评估报告解读:短寿命气候强迫因子特征及其对北极气候变化的影响
Interpretation of AMAP Assessment Reports: the characteristics of short-lived climate forcing factors and their impacts on Arctic climate change
AMAP评估报告解读:短寿命气候强迫因子特征及其对北极气候变化的影响 |
| 张玉兰, 罗犀, 康世昌, 刘治银 |
|
Interpretation of AMAP Assessment Reports: the characteristics of short-lived climate forcing factors and their impacts on Arctic climate change |
| Yulan ZHANG, Xi LUO, Shichang KANG, Zhiyin LIU |
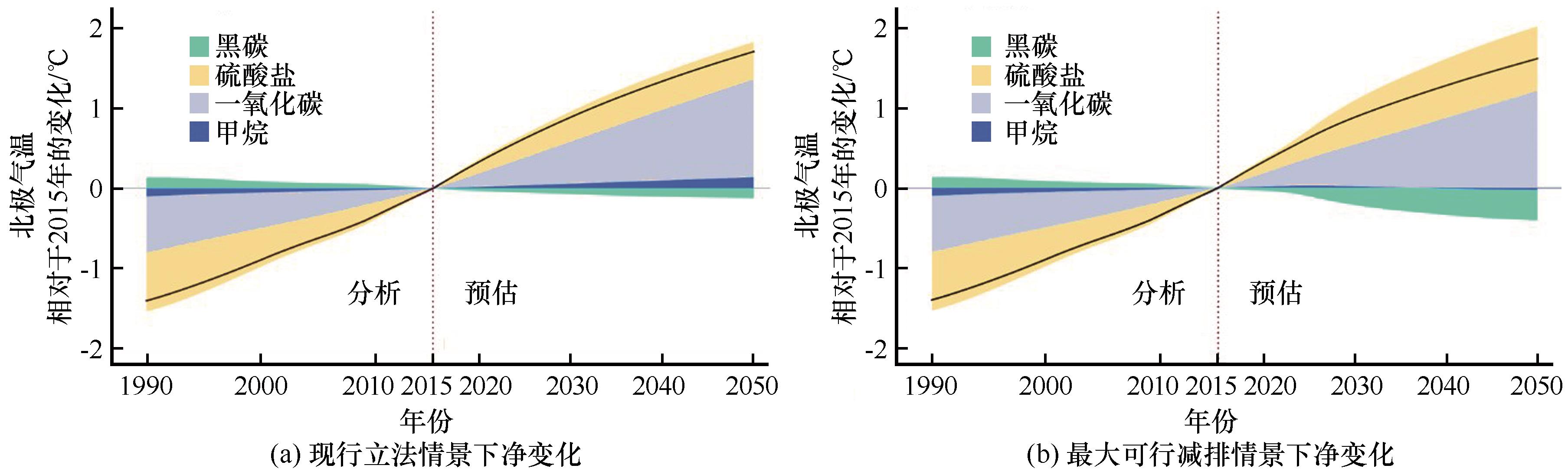
| 图7 现行立法和最大可行减排情景下北极气温相对于2015年的净变化[ |
| Fig. 7 Arctic temperature change in two different scenarios of SLCFs emissions: CLE Scenario (a) and MFR Scenario (b)[ |

|