 PDF(6549 KB)
PDF(6549 KB)


 PDF(6549 KB)
PDF(6549 KB)
 PDF(6549 KB)
PDF(6549 KB)
2000-2014年西藏雅鲁藏布江流域积雪时空变化分析及对气候的响应研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Spatiotemporal variations of snow cover over Yarlung Zangbo River basin in Tibet from 2000 to 2014 and its response to key climate factors
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}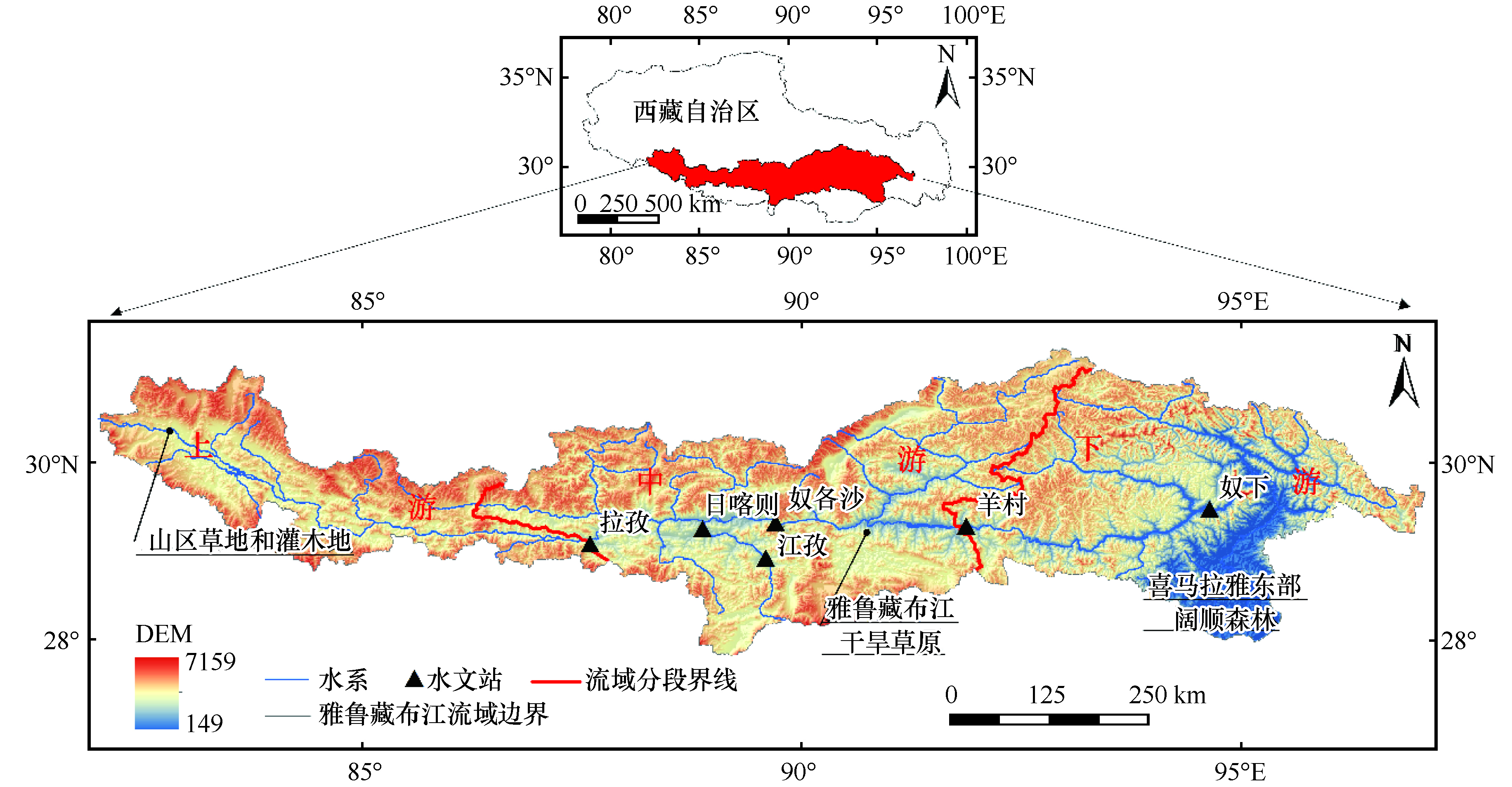
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |