Snow melting and deicing characteristics and pavement performance of active deicing and snow melting pavement
1
2019
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
主动除冰雪路面融雪化冰特性及路用性能研究综述
1
2019
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
Typical road status identification model based on pavement friction coefficient in winter pavement friction coefficient
1
2014
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
基于路面摩擦因数的冬季典型路面状态识别模型
1
2014
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
Safety evaluation model for expressway toll stations
1
2009
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
高速公路收费站安全评价模型
1
2009
... 路面积雪和结冰一直都是困扰道路交通运输行业的难题.我国有超过70%的公路在冬季会受到降雪、结冰等气候因素的影响[1].路面的积雪或结冰会显著降低路面的摩擦因数,导致车辆的滑移、制动困难和制动距离增长.路面摩擦因数在干燥的情况下为0.50~1.00,在积雪的情况则会下降到0.20~0.45,而结冰条件下更是会下降到0.15以下[2].路面摩擦因数的下降增加了交通事故的发生率,在积雪或结冰的情况下道路事故发生率会增加5~8倍[3]. ...
Impact of chemical deicers on regional environment and the charateristcs of its accumulation and translocation
1
2011
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
化学融雪剂对区域环境的影响及累积、扩散特点
1
2011
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
Environmental impact of chemical deicers-A review
2
2005
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
Freezing point test of deicers on asphalt pavement in seasonal frozen
2
2019
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
季节性冻土区沥青路面融雪剂凝冰点测试
2
2019
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Experimental analysis of highway deicers in the application of alpine areas in southwest China
2
2010
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
72012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 | | 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
西南高寒山区高速公路融雪剂适用性试验分析
2
2010
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
72012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 | | 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Overview for national standard formulation of snow-melting agent
3
2017
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
82010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 | | 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
《融雪剂》国家标准制定概况
3
2017
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
82010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 | | 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Road salt application planning tool for winter de-icing operations
4
2015
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
92010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 | | 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...
Study on salt-frost erosion of pavement concrete in salty soil area
1
2017
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
盐渍土地区道面混凝土盐冻侵蚀研究
1
2017
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Durability of bonded FRP-to-steel joints: effects of moisture, de-icing salt solution, temperature and FRP type
4
2017
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
112017 | | 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
112014 | | 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
...
112018 | 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Accumulation of de-icing salt and leaching in spanish soils surrounding roadways
2
2017
... 为克服路面积雪和结冰对道路运输的不利影响,学者们先后提出和应用了多种道路除冰雪技术.国内对道路除冰雪技术的研究始于道路融雪剂.融雪剂用于清除路面积雪始于20世纪30年代,并伴随着工业化的发展被推广开来,我国则是在20世纪70年代才开始使用融雪剂清除路面积雪[4].目前最常用的融雪剂是氯盐型融雪剂[5],包括氯化钠、氯化钾、氯化钙和氯化镁等.氯盐融雪剂以其来源广泛、成本低廉、作业简单、除雪效果明显的优点被广泛应用于冰雪清除工作[6-8],而融雪剂的大量使用造成了土壤与地下水的污染、道路附属设施的腐蚀和道路服役寿命的缩短[9-12]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
The impact of airport deicing runoff on water quality and aquatic life in a pennsylvania stream
1
1998
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
Effects of six chemical deicers on larval wood frogs (rana sylvatica)
2
2011
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Influence of pH on the toxicity of ammonia to Chironomus tentans and Lumbriculus variegatus
1
1995
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
Study on colored and environmentally friendly ice and snow-melting agent
2
2011
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
显色型环保除冰融雪剂的性能研究
2
2011
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Mechanical behaviors of asphalt mixtures in salt-wet-heat cycling
0
2016
盐-湿-热循环条件下沥青混合料的力学行为特性
0
2016
Preparation and effect of an environment-friendly snow-melting agent
0
2020
Preparation and properties of efficient and environmentally composite calcium magnesium chloride agent for snow melting
0
2019
高效环保复合型氯化钙镁盐融雪剂的制备及性能研究
0
2019
Environmental protection-type snow-melting agent from BFA compound
1
2016
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
环保型生化黄腐酸复合融雪剂的研究
1
2016
... 传统融雪剂的巨大缺陷推动了环保型融雪剂的研发、应用和发展.以醋酸钙镁盐、尿素、醇类等物质组成的非氯型融雪剂被称为环保型融雪剂.醋酸钙镁是一种应用于环保型融雪盐的添加剂[5],其融雪性能较差,但腐蚀性和毒性较小.尿素作为不含氯的有效除冰剂,对许多陆生生物是无毒的[13-14],但尿素水解形成的氨会在一定程度上危害水生生物的生存[15].相比于传统融雪剂,环保型融雪剂的腐蚀性更弱、对环境的影响也更小,但其成本高昂,不适用于大面积的路面除冰雪[16-20]. ...
Effectiveness of sodium chloride-based anti-icing filler in asphalt mixtures
1
2012
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
Low temperature property and salt releasing characteristics of antifreeze asphalt concrete under static and dynamic conditions
2
2015
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...
Research on deicing performance of asphalt mixture containing salt
1
2013
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
蓄盐沥青混合料除冰雪性能研究
1
2013
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
Experimental study on pavement performances of anti-icing asphalt mixture
1
2014
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
防冰沥青混合料路用性能试验研究
1
2014
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
Advances in asphalt pavements containing salts:additives, mixtures,performances,and evaluation
3
2019
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...
蓄盐沥青路面研究进展:盐化物材料、混合料及其性能与评价
3
2019
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...
Effects of a sodium chloride deicing additive on the rheological properties of asphalt mastic
0
2016
Preparation and characterization of anti-freezing asphalt pavement
2
2020
... 为进一步减少融雪剂对环境的影响,有学者开始从事融雪剂用量更少的融雪抑冰路面的研究.融雪抑冰路面是将融雪抑冰材料通过置换矿粉或细集料的方式添加到路面材料中的.降水后,融雪组分在渗透压的作用下释放到路表,融化路面的冰雪[21].融雪组分与路面-冰雪界面的直接接触增强了融雪效果[22].融雪抑冰路面材料的拌合和铺筑过程与普通沥青混合料基本相同,这为融雪抑冰路面的推广应用减少了困难.此外,融雪组分能够有效降低路面与冰雪界面的黏结力,为机械除冰雪提供便利.尽管融雪抑冰路面的服役年限长、经济效益好[23-24],但融雪组分的析出会导致路面性能的显著下降[25-27]. ...
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...
Model experimental study of carbon fiber heating wire for deicing and snow melting on a bridge deck
1
2020
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Demulsification of water-in-crude oil emulsion via conventional heating and microwave heating technology in their optimum conditions
2
2016
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
Laboratory investigation on microwave deicing function of micro surfacing asphalt mixtures reinforced by carbon fiber
2
2014
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
... 高杰在2014年发表的Laboratory investigation on microwave deicing function of micro surfacing asphalt mixtures reinforced by carbon fiber中对碳纤维掺量、微波频率和冰厚等影响除冰效果的因素进行分析,结果显示,冰厚在约15 mm时微波除冰的时间最短,碳纤维掺量在0.45%时,最短除冰时间缩短到了55 s[30].高杰还研究了钢丝绒、钢渣等导电相材料在微波除冰路面中的应用[76-77]. ...
Study of key technology on microwave deicing efficiency
2
2008
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
微波除冰效率关键技术研究
2
2008
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Heating asphalt mixtures with microwaves to promote self-healing
1
2013
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Investigation of the microwave absorption of asphalt mixtures containing magnetite powder
2
2019
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Engineering properties and microwave heating induced ice-melting performance of asphalt mixture with activated carbon powder filler
0
2019
Microwave heating of asphalt paving materials: principles, current status and next steps
0
2021
Laboratory investigation on deicing characteristics of asphalt mixtures using magnetite aggregate as microwave-absorbing materials
1
2016
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Snow and ice melting properties of self-healing asphalt mixtures with induction heating and microwave heating
2
2018
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Microwave induction heating of polymer-modified asphalt materials for self-healing and deicing
1
2021
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Development of automated electrical heat grid for pavement snowmelt
1
2019
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Development of anti-icing airfield pavement using surface-embedded heat wire
1
2020
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Study on heat transfer characteristics of electric heating snow melting
1
2023
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究
1
2023
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Review on technology of electric heating snow-melting pavement
1
2022
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
电热型融雪路面技术研究综述
1
2022
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Advances and development trends in eco-friendly pavements
1
2021
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Research of deicing and melting snow on airport asphalt pavement by carbon fiber heating wire
0
2020
Concrete slab installed with carbon fiber heating wire for bridge deck deicing
1
2010
... 微波除冰技术和电热除冰雪技术避免了融雪剂的使用.微波除冰技术是利用微波透过冰层作用于路面内部的吸波材料,使材料温度升高、加热路面,进而消除路面与冰层之间的冻结黏附作用,融化路面的积雪和冰层[28-30].微波除冰雪的效果主要受吸波材料、微波频率等因素的影响[31].在理想状况下,加入钢丝绒的路面在加热120 s后可升温至140 ℃[32].吸波材料的加入还能够提升路面疲劳性能、高温稳定性和耐磨性能[33-36],同时,加入的吸波材料还可用于沥青路面的自愈合[37-38].但就融雪性能而言,微波加热融雪效率低、成本较高.电热除冰雪技术是通过在路面内部埋置发热线,利用电能加热发热线,进而加热路面、融化冰雪[39-40].尽管电热除冰雪技术对环境无影响,但其融雪效果受到发热线布设参数的影响[41-42],对施工工艺要求较高.限于复杂的施工工艺、高昂的成本,目前电热除冰雪技术主要应用于机场道面、隧道进出口路面和桥面铺装[43-45]. ...
Review of technologies for snow melting systems
1
2015
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Experimental and numerical analysis of the critical heating strategy for hydronic heated snow melting airfield runway
1
2020
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Alternative hydronic pavement heating system using deep direct use of geothermal hot water
1
2019
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Experimental investigation of hydronic snow melting process on the inclined pavement
1
2010
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Techno-economic feasibility of solar water heating system: overview and meta-analysis
1
2018
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Feasibility study of snow melting system for bridge decks using geothermal energy piles integrated with heat pump in Canada
2
2019
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Optimization of hydronic heating pavement design using geothermal hot water in western north dakota
2
2021
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
Research on snow-melting mechanism in solar-heat storage in soil snow-melting systems
1
2008
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
太阳能-土壤蓄热融雪系统融雪机理的研究
1
2008
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Study on snow melting performance in solar-ground source coupled snow-melting system for pavement
1
2011
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
太阳能-土壤源热能耦合道路融雪系统融雪性能的研究
1
2011
... 流体加热除冰雪技术是目前应用较为广泛的新型除冰雪技术,已在150万m2的道路上得到应用[46].流体加热路面主要由热交换管道、传热流体以及热源组成[47].传热流体经热源加热后,通过热交换管道将热量传递至路面,融化路面积雪和冰层.常用热源有太阳能、工业废能和地热能[48-50],其中以地热能最为理想.地热能是深层地下水蕴含的能量,通过热泵将地下水泵送至换热管道.研究表明,流入热交换管道的流体温度达到60 ℃即可满足路面融雪需求[51-52].为进一步提高能量利用效果,有研究以太阳能为主要热源,将太阳能和地热能进行综合利用[53-54].流体加热除冰雪技术较撒布融雪剂和电热除冰雪技术更经济、环保,有更广阔的发展前景. ...
Investigation of design alternatives for hydronic snow melting pavement systems in China
2
2018
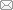
... 微波除冰技术、电热除冰雪技术和流体加热除冰雪技术等能够实现路面融雪化冰的自主性和智能性,被形象地归类为主动除冰雪技术,也被称为新型除冰雪技术.新型除冰雪技术具有环境友好、融雪效果显著、可智能控制等优点[55-59],是传统除冰雪技术不错的替代选择.但目前新型除冰雪技术种类较多、原理不一,研究方向繁多且不明确.近十余年来,我国道路除冰雪技术领域研究发展迅速,2010年以后在中国知网(CNKI)数据库和Web of Science(WoS)核心集数据库的发文量均在每年10篇以上,为进一步了解我国道路除冰雪技术领域的发展状况,本文基于CNKI数据库和WoS核心库数据,借助可视化分析软件CiteSpace对2010年以来道路除冰雪领域的文献进行了分析与讨论. ...
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
Steel fiber confined graphite concrete for pavement deicing
0
2018
Review and analysis of advances in functionalized, smart, and multifunctional asphalt mixtures
0
2021
Development and use of salt-storage additives in asphalt pavement for anti-icing: literature review
0
2021
Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures
2
2014
... 微波除冰技术、电热除冰雪技术和流体加热除冰雪技术等能够实现路面融雪化冰的自主性和智能性,被形象地归类为主动除冰雪技术,也被称为新型除冰雪技术.新型除冰雪技术具有环境友好、融雪效果显著、可智能控制等优点[55-59],是传统除冰雪技术不错的替代选择.但目前新型除冰雪技术种类较多、原理不一,研究方向繁多且不明确.近十余年来,我国道路除冰雪技术领域研究发展迅速,2010年以后在中国知网(CNKI)数据库和Web of Science(WoS)核心集数据库的发文量均在每年10篇以上,为进一步了解我国道路除冰雪技术领域的发展状况,本文基于CNKI数据库和WoS核心库数据,借助可视化分析软件CiteSpace对2010年以来道路除冰雪领域的文献进行了分析与讨论. ...
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature
1
2006
... CiteSpace是由陈超美教授开发的一款用于文献计量分析的可视化软件,软件可以基于CNKI数据库和WoS核心集导出的文献信息对文献的关键词、发文作者、发文机构和文献来源期刊等数据进行分析,通过分析结果的可视化展现,可以直观地表现出学科领域的发展脉络、研究热点和发展方向[60-62]. ...
Visualizing and exploring scientific literature with CiteSpace
1
2018
... Publications volume information of major research institutions
Table 1| 机构名称 | 中文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 | 机构名称 | 英文文献发文量/篇 | 首次发文年份 |
|---|
| 长安大学 | 49 | 2010 | 长安大学 | 61 | 2014 |
| 重庆交通大学 | 12 | 2010 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 33 | 2012 |
| 哈尔滨工业大学 | 10 | 2011 | 武汉理工大学 | 29 | 2011 |
| 长沙理工大学 | 9 | 2015 | 中国科学院 | 25 | 2012 |
| 武汉理工大学 | 9 | 2010 | 东南大学 | 16 | 2011 |
| 内蒙古工业大学 | 8 | 2011 | 吉林大学 | 14 | 2010 |
| 吉林大学 | 8 | 2010 | 中国地质大学 | 11 | 2018 |
| 山西省交通科学研究院 | 7 | 2013 | 合肥工业大学 | 11 | 2017 |
| 交通运输部公路科学研究院 | 7 | 2012 | 同济大学 | 11 | 2014 |
| 中交第一公路勘察设计研究院 | 6 | 2010 | 中国科学院大学 | 11 | 2018 |
从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature
1
2017
... CiteSpace是由陈超美教授开发的一款用于文献计量分析的可视化软件,软件可以基于CNKI数据库和WoS核心集导出的文献信息对文献的关键词、发文作者、发文机构和文献来源期刊等数据进行分析,通过分析结果的可视化展现,可以直观地表现出学科领域的发展脉络、研究热点和发展方向[60-62]. ...
Influence of environmental temperature on road de-icing efficiency using microwave
1
2008
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
环境温度对道路微波除冰效率的影响
1
2008
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Efficiency analysis on microwave-enabled road deicing in winter
1
2008
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
冬季道路微波除冰效率研究
1
2008
... 从中文核心文献和WoS核心文献分析结果看,长安大学、哈尔滨工业大学和武汉理工大学是国内道路除冰雪领域研究的重要力量,其中长安大学在中文核心期刊和WoS核心集上的发文量均较突出.长安大学早期对道路除冰雪技术的研究主要集中在除冰机械、融雪剂的影响等方面.2008年,长安大学发表了多篇微波除冰雪技术相关的文献,对微波除冰雪的融雪效果、影响除冰效果的关键因素等进行研究[31,63-64].2014年,长安大学首次在WoS核心集期刊上发表了道路除冰雪技术相关的论文Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures,文章通过体积置换法将混合料中的细集料或矿粉置换为防冻填料,研究了防冻沥青混合料的稳定性、高低温性能和抗冻性能[59]. ...
Research progress on the performance of induction heating asphalt mixture for melting snow and deicing
1
2021
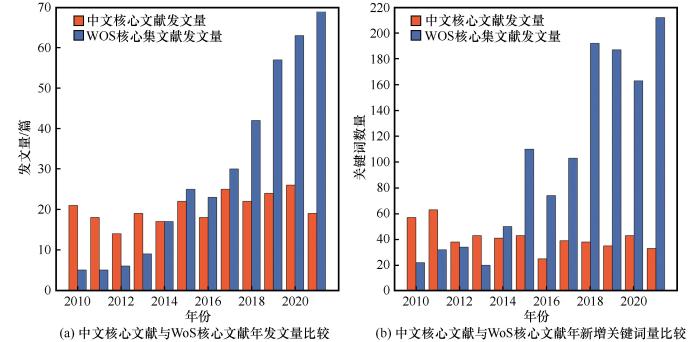
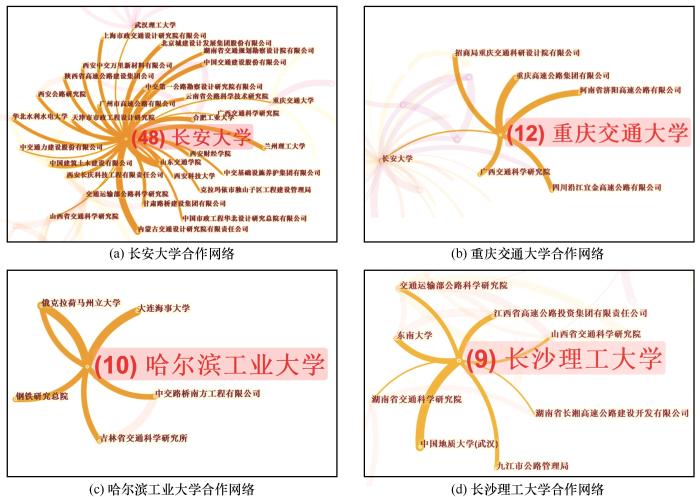
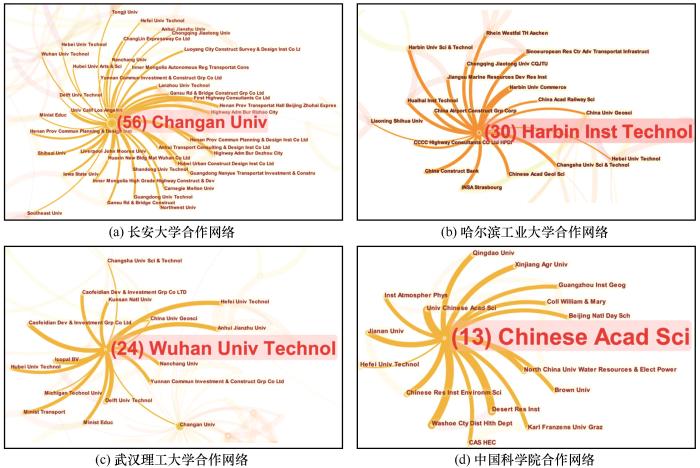
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
感应加热沥青混合料融雪化冰性能研究进展
1
2021
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
Coating material for environmental sustained release active melting of ice and snow
0
2020
Microwave sensitive coating materials and equipment for snow removal
0
2018
Research on the factors influencing hydrophobic properties of antifreezing material
0
2013
Current situation and development of deicing technology with built-in carbon-fiber heating wires
1
2016
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
内置碳纤维发热线融冰技术的现状与发展
1
2016
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
Laboratory and numerical investigation of microwave heating properties of asphalt mixture
1
2019
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
Material characterization to assess effectiveness of surface treatment to prevent joint deterioration from oxychloride formation mechanism
1
2019
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
Preparation of super-hydrophobic anti-icing coating for asphalt pavement and evaluation of its anti-icing properties
1
2021
... 从中文核心文献发文机构的分析结果中可以看到,长安大学与其他单位合作广泛,与众多的高校、企业和研究院均有合作关系,其合作包括环保型融雪剂、融冰雪涂层、融雪抑冰路面、微波除冰、电热除冰等领域[65-69].重庆交通大学、哈尔滨工业大学和长沙理工大学与其他单位的合作相对集中.四所高校在中文论文领域的合作者主要以国内单位为主;同时,四所高校均与工程单位有合作,针对不同道路除冰雪技术的融雪性能、对路用性能的影响等方面进行研究.WoS核心集文献的分析结果显示各研究单位的对外合作均有所增强.作为发文量最高的研究单位,长安大学的合作网络也最为复杂,其合作关系更是涉及了代尔夫特理工大学[70]、爱荷华州立大学[71]、卡内基梅隆大学[72]等国外高校. ...
Design and performance of an asphalt pavement snow melting system
1
2011
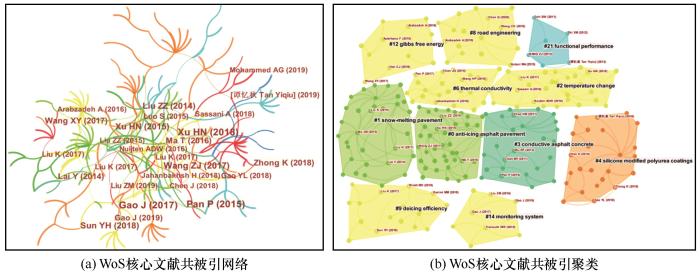
... 图6(a)中的每个节点代表一篇文献,标签为文献对应的作者和发表时间,图中显示的标签是被引次数大于7次的文献作者.图谱中的文献共被引次数大于20次的文献作者有潘攀、高杰和徐慧宁,其研究方向均集中在新型除冰雪技术的研究与应用.潘攀在2011年发表的论文Design and performance of an asphalt pavement snow melting system中对太阳能集热沥青路面融雪的可行性进行了研究[73].太阳能集热沥青路面可通过吸收太阳能来加热埋设在路面内部的管道中的流体,并在有融雪化冰需要时将能量释放出来[74],在路面中添加碳纤维不但可以提高混合料性能,而且可以将路面的导热系数提高30%以上[75]. ...
Simulation study of heat energy potential of asphalt solar collectors
1
2014
... 图6(a)中的每个节点代表一篇文献,标签为文献对应的作者和发表时间,图中显示的标签是被引次数大于7次的文献作者.图谱中的文献共被引次数大于20次的文献作者有潘攀、高杰和徐慧宁,其研究方向均集中在新型除冰雪技术的研究与应用.潘攀在2011年发表的论文Design and performance of an asphalt pavement snow melting system中对太阳能集热沥青路面融雪的可行性进行了研究[73].太阳能集热沥青路面可通过吸收太阳能来加热埋设在路面内部的管道中的流体,并在有融雪化冰需要时将能量释放出来[74],在路面中添加碳纤维不但可以提高混合料性能,而且可以将路面的导热系数提高30%以上[75]. ...
Study on volume performance of conductive asphalt concrete based on freeze-thaw cycle
1
2013
... 图6(a)中的每个节点代表一篇文献,标签为文献对应的作者和发表时间,图中显示的标签是被引次数大于7次的文献作者.图谱中的文献共被引次数大于20次的文献作者有潘攀、高杰和徐慧宁,其研究方向均集中在新型除冰雪技术的研究与应用.潘攀在2011年发表的论文Design and performance of an asphalt pavement snow melting system中对太阳能集热沥青路面融雪的可行性进行了研究[73].太阳能集热沥青路面可通过吸收太阳能来加热埋设在路面内部的管道中的流体,并在有融雪化冰需要时将能量释放出来[74],在路面中添加碳纤维不但可以提高混合料性能,而且可以将路面的导热系数提高30%以上[75]. ...
Utilization of steel slag as aggregate in asphalt mixtures for microwave deicing
1
2017
... 高杰在2014年发表的Laboratory investigation on microwave deicing function of micro surfacing asphalt mixtures reinforced by carbon fiber中对碳纤维掺量、微波频率和冰厚等影响除冰效果的因素进行分析,结果显示,冰厚在约15 mm时微波除冰的时间最短,碳纤维掺量在0.45%时,最短除冰时间缩短到了55 s[30].高杰还研究了钢丝绒、钢渣等导电相材料在微波除冰路面中的应用[76-77]. ...
Microwave deicing for asphalt mixture containing steel wool fibers
1
2019
... 高杰在2014年发表的Laboratory investigation on microwave deicing function of micro surfacing asphalt mixtures reinforced by carbon fiber中对碳纤维掺量、微波频率和冰厚等影响除冰效果的因素进行分析,结果显示,冰厚在约15 mm时微波除冰的时间最短,碳纤维掺量在0.45%时,最短除冰时间缩短到了55 s[30].高杰还研究了钢丝绒、钢渣等导电相材料在微波除冰路面中的应用[76-77]. ...
Development and testing of heat-and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement
1
2012
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
Study on the heat and mass coupled snow melting model for solar-ground source coupled heated pavement
1
2014
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热道路融雪系统融雪模型的建立
1
2014
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
Simulation analysis of snow melting characteristics of solar-ground source coupled snow-melting system for pavement
1
2015
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
太阳能-土壤源热能复合道路融雪系统融雪特性的仿真分析
1
2015
... 徐慧宁在Development and testing of heat- and mass-coupled model of snow melting for hydronically heated pavement中建立了流体加热路面融雪模型,并对模型的准确性进行了验证[78],其研究还表明在冬季蒸发率和加热功率较小的条件下融雪极易产生二次冻结[55].随后,徐慧宁等人还建立了由热泵、换热管等组成的太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热路面融雪系统,并利用模型分析了环境温度、雪层厚度、输入热功率等融雪条件对融雪过程中各阶段融雪特性的影响[79-80]. ...
Prediction models of the thermal field on ice-snow melting pavement with electric heating pipes
1
2017
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
Influence factor of thermal conductivity of cement concrete and its prediction model
1
2012
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
水泥混凝土导热性能影响因素及预估模型研究
1
2012
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
The accumulated stress damage and residual life prediction of unreinforced concrete pavement with electric heating pipes
1
2021
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
The equivalent plasticity strain analysis of snow-melting heated pavement concrete exposed to inner elevated temperatures
1
2017
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
Multi-objective optimization of the design and operation for snow-melting pavement with electric heating pipes
2
2017
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Design of electric heat pipe embedding schemes for snow-melting pavement based on mechanical properties in cold regions
1
2019
... 刘凯有三篇论文的共被引次数大于7次,其研究方向主要集中在电热融雪技术方面,并先后对电热融雪路面的温度场分布[81-82]、路面性能变化[83-84]、融雪路面设计[85-86]等内容进行了研究. ...
Study on effectiveness of anti-icing and deicing performance of super-hydrophobic asphalt concrete
1
2018
... 在高共被引文献中,与融雪抑冰路面、电热除冰雪、流体加热除冰雪和微波除冰雪相关的论文数量分别为6篇、4篇、4篇和4篇.值得一提的是,分析结果中还出现了与超疏水涂层相关的文献Study on effectiveness of anti-icing and deicing performance of super-hydrophobic asphalt concrete,文献对超疏水沥青混凝土在不同工况下的防冰、除冰性能进行了研究,结果表明超疏水涂层能够有效地促进水滴在表面的运动,降低路面与冰层之间的黏附力[87]. ...
Optimization design and prediction of the snow-melting pavement based on electrical-thermal system
1
2022
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
All-organic superhydrophobic coatings with mechanochemical robustness and liquid impalement resistance
1
2018
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
The anti-icing and mechanical properties of a superhydrophobic coating on asphalt pavement
1
2018
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Snow melting on the road surface driven by a geothermal system in the severely cold region of China
1
2020
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Numerical analyses of a laboratory test of a geothermal bridge deck externally heated under controlled temperature
1
2020
... 目前新型除冰雪技术的研究已成为领域内的研究前沿.新型除冰雪技术的种类较多,融雪原理不一,应用前景也各不相同.电热除冰雪技术对环境的影响较小、可以实现智能控制,但其施工工艺复杂、对能量的需求较大[37,85,88].在路面表面涂覆超疏水涂层可以有效地延长结冰时间、降低路面-冰层的黏结力,但超疏水涂层强度低、与基体间的附着力小、经济性差,极易在夏秋季节的高温条件下损坏,还会影响路面抗滑性能[89-90].作为目前应用最广泛的新型除冰雪技术,流体加热路面可以利用更易获取的地热能、太阳能和工业废能作为热能来源[51,91-92],合理设计流体加热路面还能够实现夏季吸收路面热量、冬季释放热量融化冰雪的功能. ...
Design, construction, and evaluation of energy-harvesting asphalt pavement systems
1
2020
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
Wettability patterning for high-rate, pumpless fluid transport on open, non-planar microfluidic platforms
1
2014
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
Large-scale fabrication of translucent and repairable superhydrophobic spray coatings with remarkable mechanical, chemical durability and UV resistance
0
2017
Inexpensive and non-fluorinated superhydrophobic concrete coating for anti-icing and anti-corrosion
1
2019
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
A review on hydronic asphalt pavement for energy harvesting and snow melting
1
2015
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
Analyzing the performance and control of a hydronic pavement system in a district heating network
1
2019
... 综合来看,电加热除冰雪技术对电能需求较大,电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合和节能设计能够有效地推动电热融雪路面的推广应用.如我国西北地区风能、太阳能等可再生能源资源丰富,且冬季又常常受到冰雪灾害的困扰,可在西北地区自然资源丰富的关键路段开展电热除冰雪技术与可再生能源结合应用[93].另一方面,对电热除冰雪路面的合理设计和路面材料的合理选取也能减少能量的损耗、提高能量利用率.超疏水涂层的应用会影响到交通的安全运行,可以研究成本更低、生命周期更短、时效性更强的一次性超疏水涂层,既保证原有超疏水涂层的功能,又避免涂层对路面功能的影响[94-96].流体加热融雪技术对流体的温度有一定要求,可以研究利用地热能、工业废能、太阳能与电能结合综合供能的方式提高能量利用率[52,97].高昂的运行成本限定了新型除冰雪技术的大面积应用,可建立新型除冰雪技术与机械除冰雪综合应用的除冰雪方法,即运用新型除冰雪技术消除路面与冰雪界面的黏结,使机械除冰雪的效率更高、对路面的损坏更小[29,98]. ...
How common road salts and organic additives alter freshwater food webs: in search of safer alternatives
1
2017
... 目前对融雪剂的研究占比依然很大,但已不再是研究前沿,且大量研究集中于环保型融雪剂和融雪抑冰路面.受经济条件、能量供应和地理位置的限制,大量的地区无法应用新型除冰雪技术,对环保型融雪剂的开发仍旧是重要研究内容[9,99].融雪抑冰路面中融雪抑冰材料的添加与释放会对路面性能造成严重影响,融雪抑冰材料的释放速率控制和对混合料性能的影响仍旧是亟待解决的问题[22,25,27]. ...


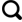

 甘公网安备 62010202000676号
甘公网安备 62010202000676号